What is Cloud Computing?
What is Cloud Computing?
Before entering into the world of Cloud Computing, we must have
knowledge about the In-Premises Datacenter. In-premises DC
means you will have a proper room with equipped devices like
Servers, Networking Devices, Storage Devices, Power Devices,
and Cooling Devices etc. And for that you need Cost and it is
of two types CaPex and OPex.
CaPex means you need a Capital Investment at the time of
setting up your DC for purchasing the devices or etc. While
OPex stands for Operational Cost which you are requiring during
your maintenance of DC like if there is any failure in devices,
electricity costs, maintenance cost, etc.
The OPex can be planned or unplanned. If there is any failure
at DC then it will make your running services down.
The In-premises DC includes lots of things like Cost, Effort,
Maintenance and monitoring etc.
Now let’s have a look to Cloud Computing. It is basically a
model of IT infrastructure where you can use or retrieve
resources over internet through web-bases tools irrespective
if underlying it. If we talk about Azure then you can access it
via its portal “portal.azure.com” to access its resources.
Let’s have a look to below images to understand how a user
access it resource.
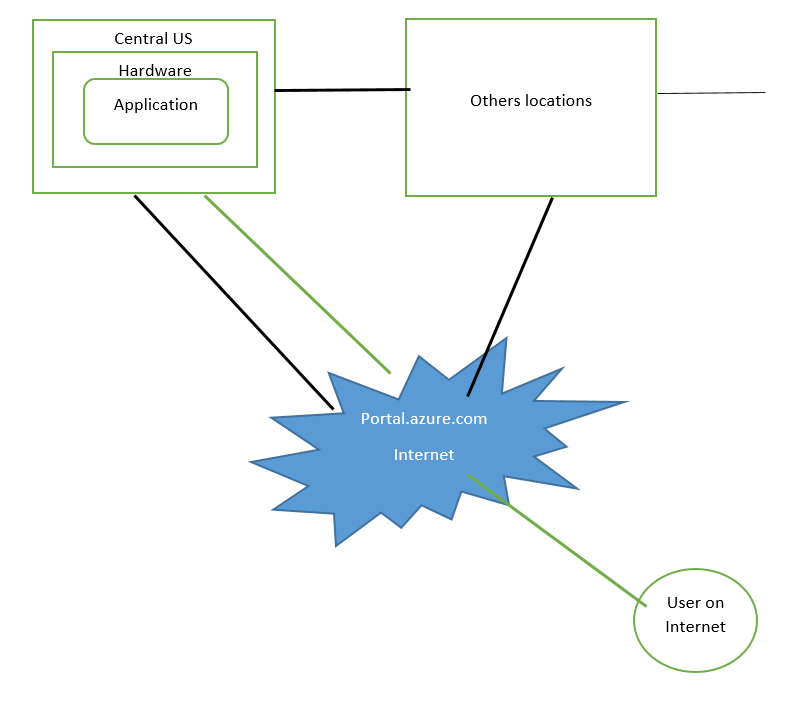
If you will see above screen then you can see that “Central
India” is DC for Azure which is connected to Internet and
exposed to “portal.azure.com”. So if any user on internet
looking for an application. He can go to Azure portal via
internet and can build a VM and install application and
accordingly he can pay to Microsoft. So user don’t need to buy
any hardware and other stuffs related to In-premise DC.
If you want to define the Cloud Computing then it is delivery
of computing services like serves, storage, networking,
software, applications etc. over internet “in cloud”. This is
always available on demand. You don’t look for buying hardware,
installing and configuring it. You need to just look for your
requirement and buy it.
It has three types of deployment models.
Public Cloud: Services are available to users over internet.
Private Cloud: Cloud infrastructure configured solely for an
organization.
Hybrid Cloud: This includes both clouds private and public and
where data can be accessed between them.
Let’s have go through some benefits of Cloud Computing.
The important thing is that you need to pay what you are
using as pay-as-you-go subscription. So you can optimize
your cost as per your application requirement. Like if you
are using any VM or application for some hours and now you
don’t need it. You can delete that and pay what you have
used.The other important benefit is Scalability. Your resources
are liable to scale up and scale down as per your
requirement in a matter of time. You don’t need to look for
quotes of hardware to buy and install it. This is of two
types: Horizontal and Vertical. Vertical scaling means you
can increase or decrease your hardware like RAM, CPU etc.
when you needed. In case of horizontal scaling, you can
take an example of web application. If your application is
running over two machine and in a matter of time your
utilization increases then you can go ahead and add one
or two more VMs to scale it up. And when its utilization
is normal you can release them also. Here you need to pay
for the extra VMs only for that time.You can configure required security and also enhance it by
lot services provided by Cloud Services. There are lots of
agencies which always audits cloud services.You can also configure scaling automatically so that your
intervention is not required at the time of need. This is
called Elasticity. There is a small difference between
elasticity and scaling and that is it. Elasticity has the
ability to adjust the resources as per your requirement.It is reliable for data security, availability etc.
Related
0
Votes
3
Ans
How to Switch Java Version on Linux Using Alternatives Command
1.62K viewsvarelite Changed status to publish
Question and answer is powered by anspress.net
Loading repositories and latest updates...
Recent Posts
Recent Blog
- heating_impn on Installation of Linux Operating System (Red Hat 8) in VMWare Workstation
- global_xvPn on Installation of Linux Operating System (Red Hat 8) in VMWare Workstation
- 2jl on In Azure: Canonical Ubuntu Issue Impacted VMs and AKS
- 2jl on In Azure: Canonical Ubuntu Issue Impacted VMs and AKS
- 2jl on What is Cloud Computing?
Interview Q&A
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- March 2025
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- November 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
 Visit My GitHub VARELITE
Visit My GitHub VARELITE
It’s fascinating how platforms like 2jl club are prioritizing secure access & verified accounts – crucial for responsible gaming & data integrity. RNGs are key, but KYC feels essential too! 🤔