Junos
Junos
Junos kernel is basically based on FreeBSD unix os. It is an
open source software. This is feature-rich network operating
system which has been using in a very wide range of Juniper
Devices which includes switches, routers etc. It function into
multiple software processes and each process handles a device
function. This functionality enhances its stability, isolation
etc.
The primary module of Junos are “Routing Engine (RE)” and
“Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE)”.
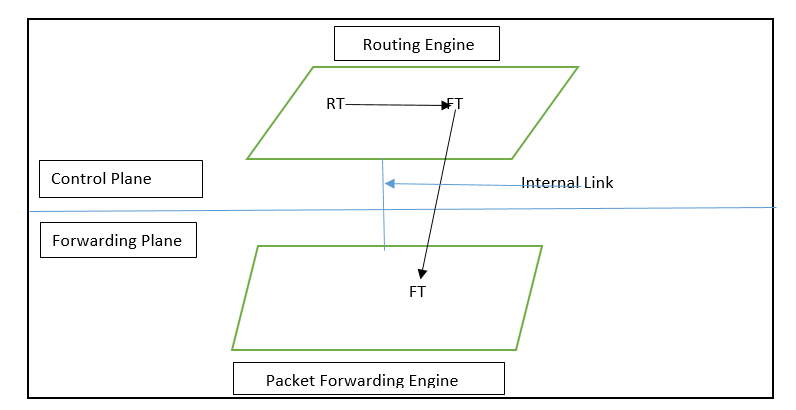
The Routing Engine is called as brain of Junos as it has
important responsibility like Routing Protocols, Control Plane
Processing, Network Management, etc. It handles CLI (Command
Line Interface) functionality as well. You can say it is
basically used for System Management. It maintains routing
tables, bridging tables, forwarding tables etc. If you will see
the below image then you can see that RT (Routing table) which
is task of RE. It also create a forwarding routing table (FT)
which keeps active routes details and send a copy of this to
Forwarding Engine.
It also controls chassis component, system management,
interfaces and access to device. As I mentioned earlier it is
also responsible for CLI and J-Web GUI.
If we talk about “Packet Forwarding Engine” then it handles
function related to Packet forwarding, Quality of Service
(QoS), Packet Filtering, rate limiting, Class of Service (CoS),
stateless firewall, etc. This is basically run on separate
hardware and in some case it runs on Application Specific
Integrated Circuits (ASICs) for increased performance. ASICs
is just a specified hardware. It receive the routing table
from RE with an internal link between RE and PFE.
As we know that each process runs in its own space and is
called Protocol Daemons. Each daemon has its specific function.
Like rpd (Routing Protocol Daemon), mgd (Management Daemon),
dcd (Device Control Daemon), alarmd (Alarm Daemon), syslogd
(System Log Daemon), etc.
Difference between Transit and Exception Traffic
Traffic that enters from an ingress port which compared with
forwarding table and then forwarded out to an egress port is
called Transit Traffic. Ingress and Egress ports in networking
refers to the directions in which data packets are entering or
existing from network devices like router, switch, firewall
etc. Ingress port is basically the network port from where
data packets enters while Egress port is the network port from
data packet exit to a network. If we are forwarding a traffic
then forwarding table must have the entry of destination.
Transit traffic is handled by Forwarding Plane.It can be
unicast or multicast traffic.
Exception Traffic does not pass through the local devices and
it requires a special handling. When Junos device is the
destination of the traffic which is called Exception Traffic.
Like if you want to ping Junos device or you want to do “ssh”
or “telnet” Junos devices. These are exception traffic. You
need to remember that traffic will always come to Forwarding
Plane and if its towards Junos then it will forwarded it to
Junos otherwise will forward as per forwarding table. If it is
going to Junos then Internal link is used to traffic point.
Related
0
Votes
3
Ans
How to Switch Java Version on Linux Using Alternatives Command
1.63K viewsvarelite Changed status to publish
Question and answer is powered by anspress.net
Loading repositories and latest updates...
Recent Posts
Recent Blog
- heating_impn on Installation of Linux Operating System (Red Hat 8) in VMWare Workstation
- global_xvPn on Installation of Linux Operating System (Red Hat 8) in VMWare Workstation
- 2jl on In Azure: Canonical Ubuntu Issue Impacted VMs and AKS
- 2jl on In Azure: Canonical Ubuntu Issue Impacted VMs and AKS
- 2jl on What is Cloud Computing?
Interview Q&A
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- March 2025
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- November 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
 Visit My GitHub VARELITE
Visit My GitHub VARELITE